Skew is defined as the difference between the Arrival Time of the Clock Signal at the Clock pin of the Capture Flop and the Launch Flop.
(Arrival Time at Capture Flop Pin – Arrival Time at Launch Flop Pin)
Based on the above expression Skew can be of three types:-
- Positive Skew
- Negative Skew
- Zero Skew
- Local Skew
- Global Skew
Positive Skew
If the Clock Signal arrives at the Clock Pin of Launch Flop first and Clock Pin of Capture Flop later it is known as Positive Skew. Positive Skew relaxes Setup Check as Data will get extra time to be stable. But, it tightens the Hold check as the Data has to be kept stable for more time equal to Clock Skew. Refer Fig.1
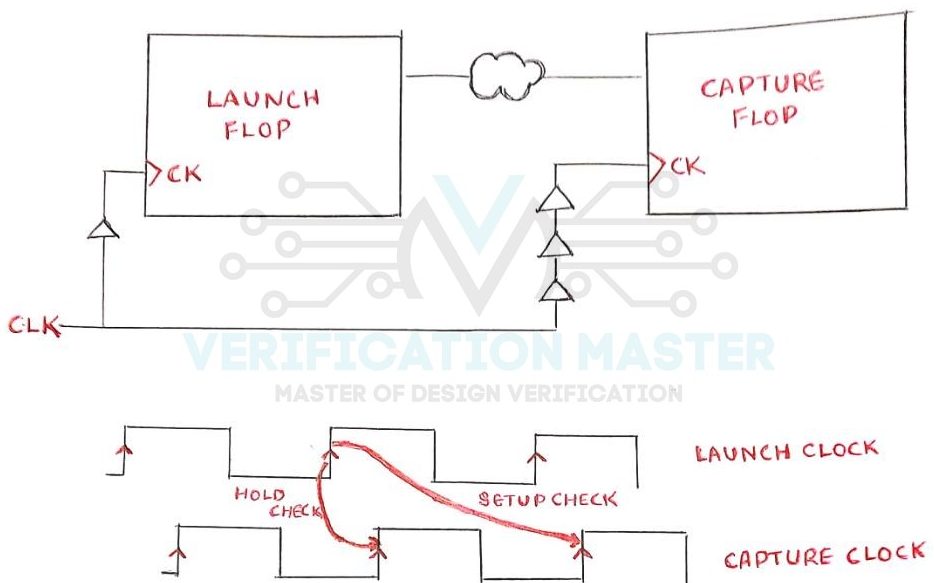
Fig. 1: Positive Skew
Negative Skew
If the Clock Signal arrives at the Clock Pin of Capture Flop first and Clock Pin of Launch Flop later it is known as Negative Skew. Negative Skew relaxes Hold check as the Data has to be kept stable for less amount of time. But, it tightens the Setup check as the Launch Flop is getting Clock Signal later than Capture Flop so the Data Signal will get less time to travel from Launch Flop to Capture Flop. Refer Fig.2
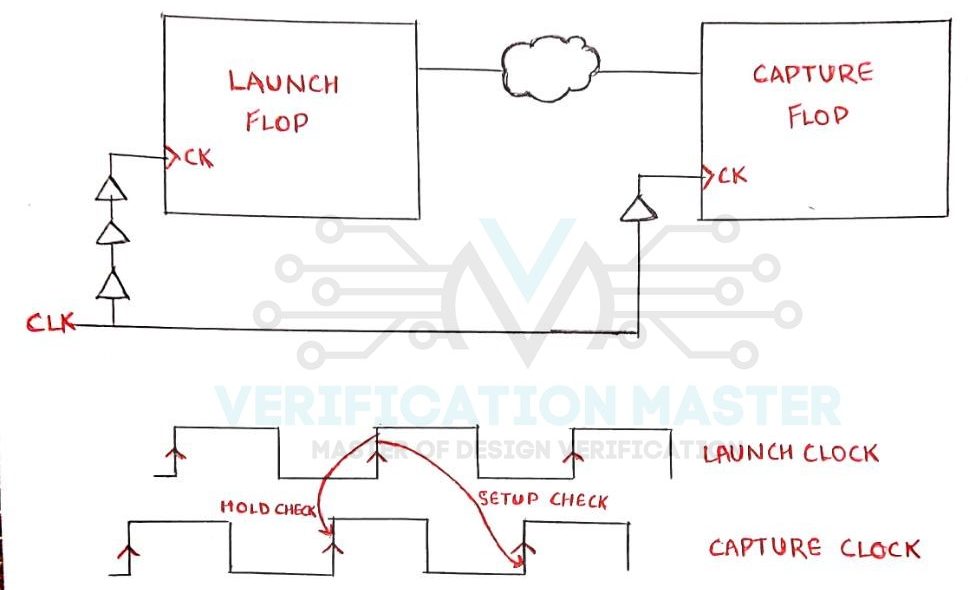
Fig. 2: Negative Skew
Zero Skew
If the Clock Signal arrives at the Clock Pin of Launch Flop and Capture Flop at the same time it is known as Zero Skew. Practically Zero Skew is not possible as there is always a certain amount of Delay between two Flops.
Local Skew
Skew between two back-to-back Flops is known as Local Skew.
Global Skew
Skew Between two non-related Flops is known as Global Skew.
From this blog you can answer the below set of questions:
- Q1) What is Clock Skew?
- Q2) What is a Positive Skew?
- Q3) What is Negative Skew?
- Q4) What is Zero Skew?
- Q5) What are Local and Global Skew?

