In every Circuit, there is a Clock Source and Clock Sinks. As every Flop is activated by a Clock Signal so Flops are the Sinks for Clock Signal. However, the Clock Signal takes some time to travel from its Source Point to the Sink Point. In short “Latency is defined as the time taken by the Clock Signal to travel from its Source Point to Sink Point”
Types of Latency
Fig. 1: Types of Latency
Clock Latency = Source Latency + Network Latency
Source Latency
It is defined as the amount of time a Clock Signal takes to travel from a Clock Source say a PLL to reach to Clock Definition Point of the Chip. It is also known as Clock Insertion Delay. Refer Fig.2
Network Latency
It is defined as the amount of time the Clock Signal takes to travel from the Clock Definition Point of the Chip to reach the Clock Sink Points or Flops. Every Sink Point in a Circuit has a different Network Delay based on the location of the Sink Point from the Clock Definition Point. It is also known as Network Insertion Delay. Refer Fig.2
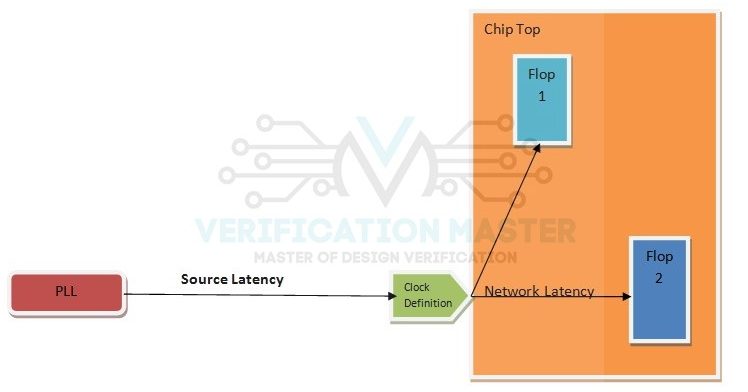
Fig. 2: Example of Source and Network Latency
NOTE: Sum of Source Latency and Network Latency for all Flops/Sink points should be equal for a balanced clock tree.
Significance of Latency
Latency means the total time taken by the Clock Signal to reach from the Clock Source to Clock Sink points. Now, if the Clock is reaching late or early at the Clock Sink points, then in that case timing will be affected because here Insertion Delay is getting affected. To balance the Insertion Delay we will insert more and more Buffers to minimize the Insertion Delay which is the prime objective of the CTS stage.
Pre-CTS and Post CTS Latency
Before CTS (Clock Tree Synthesis) the clock is ideal. So, Latency is also ideal before CTS. Insertion Delay is clock latency after CTS. Clock Latency is a virtual delay while Insertion delay is an actual/physical delay. Latency is the design’s clock target defined in SDC (Synopsys Design Constraint) file while insertion delay is achieved a delay after CTS.
Commands to Specify Latency
Network Latency
set_clock_latency <value> CLK
Source Latency
set_clock_latency <value> CLK -source
So, from this blog you can answer the below set of questions:
- Q1) What is Clock Latency?
- Q2) What are the categories of Clock Latency?
- Q3) Define Source Latency and Network Latency.
- Q4) Explain Pre CTS and Post CTS Latency.
- Q4) Write commands to specify Source Latency and Network Latency.